Inverted T Waves
ISCHEMIA
- Localized
- Deep, symmetrical (V-shaped)
- Biphasic (positive-negative)
- ST segments frequently at baseline (isolated T wave inversion without ST depression)
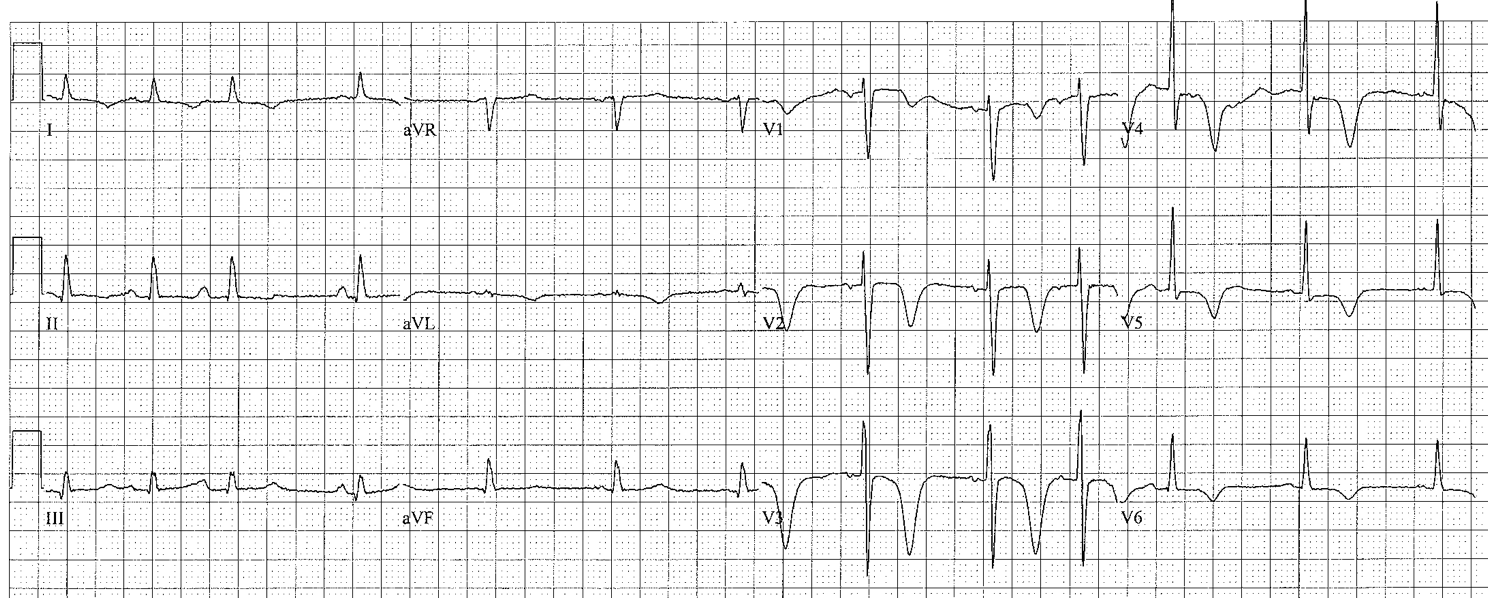
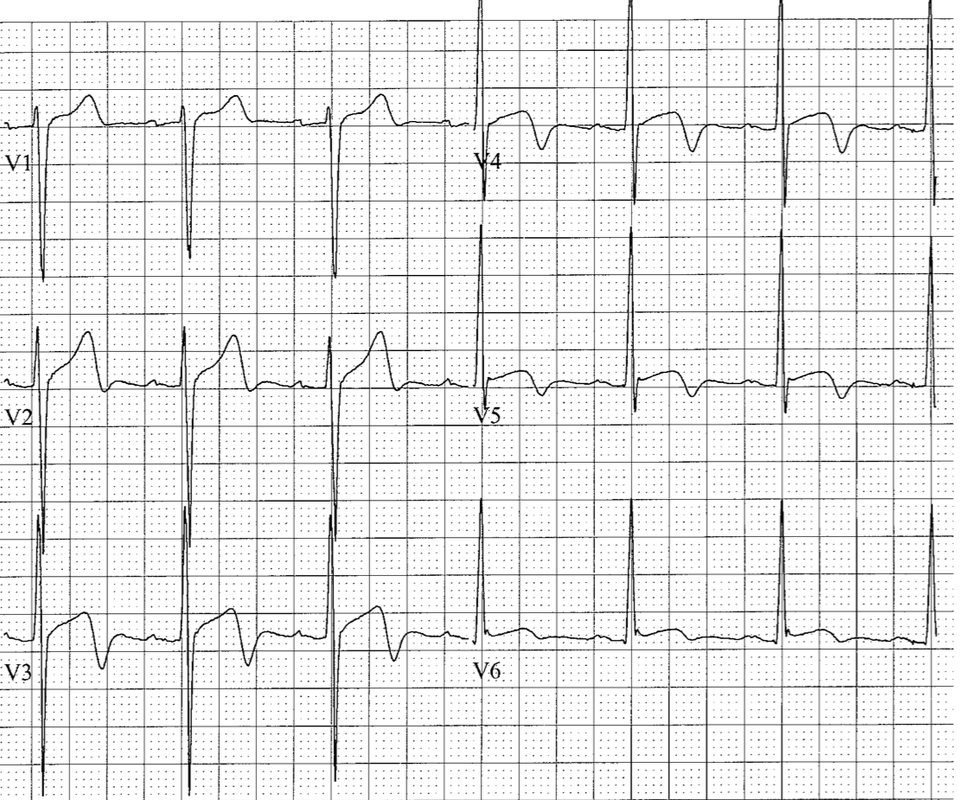
STRAIN
LV strain: seen in left leads (I, aVL, V5-V6) – usually in association with LVH
- Strain pattern: upsloping ST depression followed by non-symmetrical T wave inversion (shallow downslope, rapid upslope)
LV strain: seen in left leads (I, aVL, V5-V6) – usually in association with LVH
RV strain: seen in anterior precordial leads (V1-V3) – differential diagnosis includes anterior ischemia
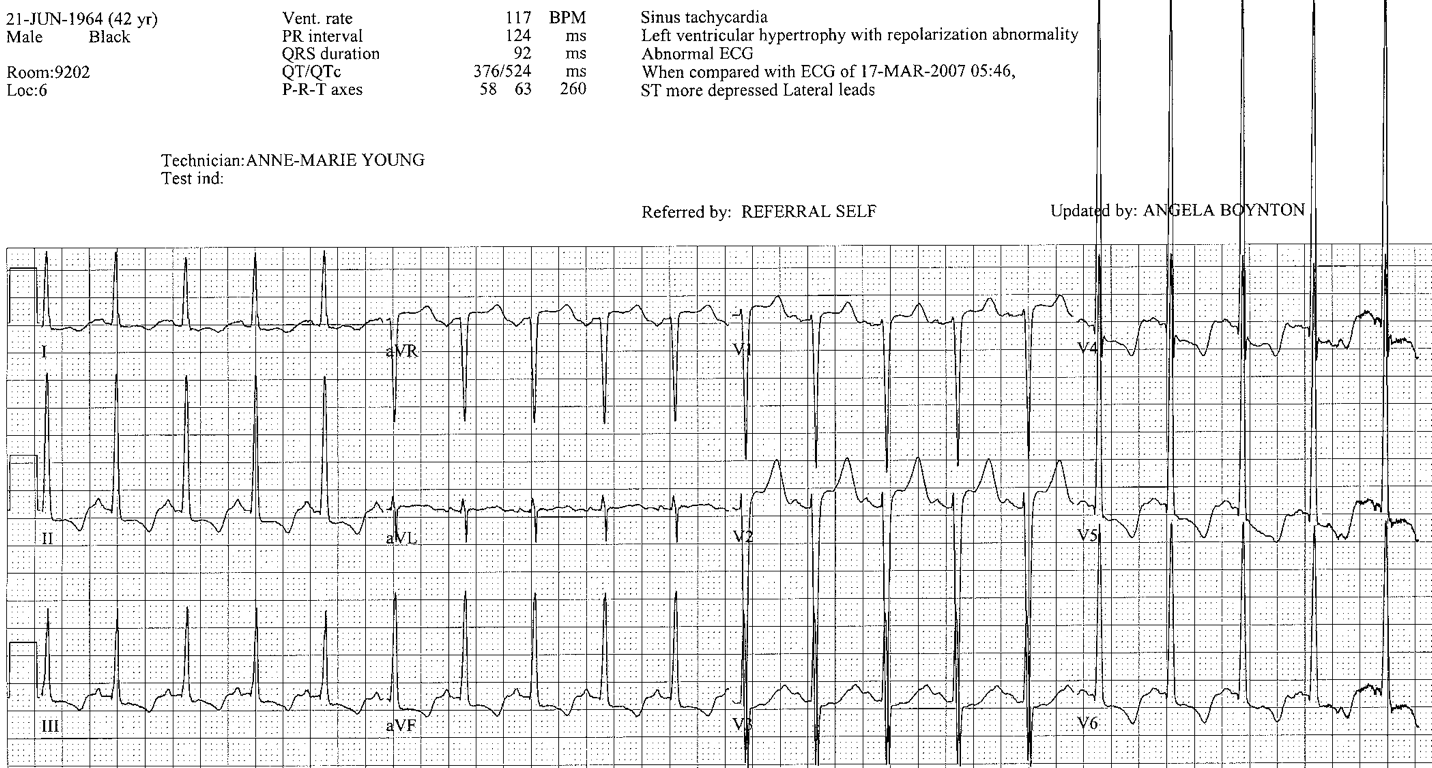
INJURY AND NONSPECIFIC
- Diffuse
- May be shallow
- May be deep and wide
- May be associated with QT prolongation
- Causes: ischemia; electrolyte abnormalities; drug toxicity; acute CNS event; catecholamine effect; pulmonary edema; massive PE
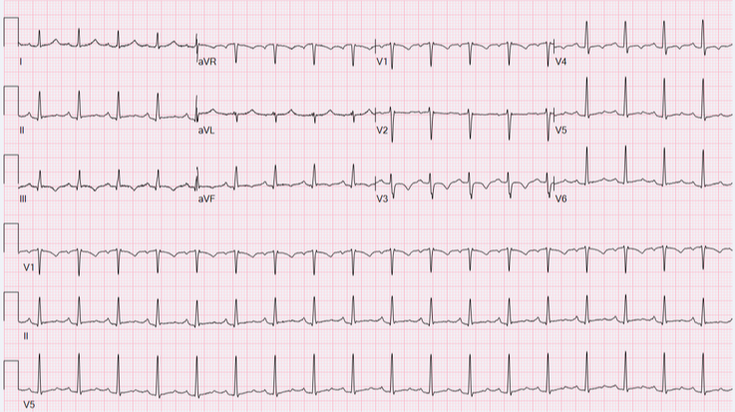
CARDIAC MEMORY
- Seen in patients with intermittent wide complex rhythms: intermittent pacing, LBBB, WPW
- When the QRS becomes narrow, T waves are inverted in those leads which had downgoing QRS complexes during the wide complex rhythm
- Duration of memory Ts mimics duration of previous Wide complex rhythm
- Frequently associated with prolonged QT
The T waves are the most sensitive but least specific markers in the ECG!
(almost anything can turn them down)
(almost anything can turn them down)