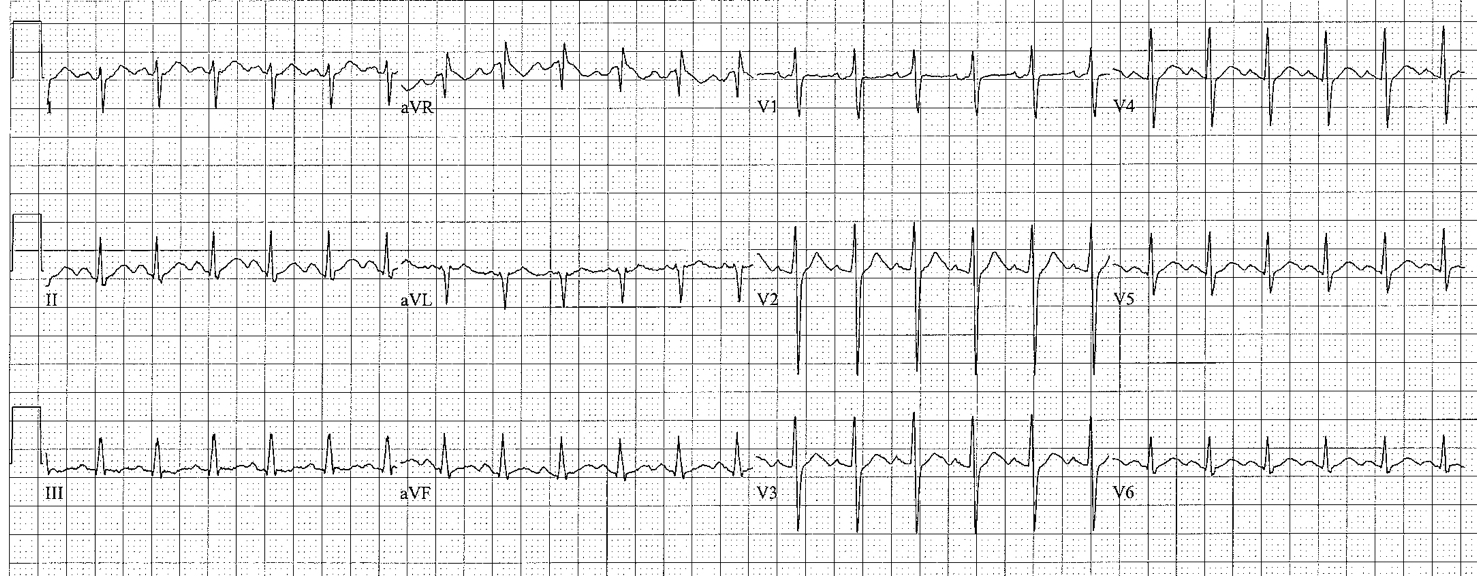
Right Axis Deviation
Causes of right axis deviation
- Young age
- RVH, pulmonary hypertension, COPD, secundum ASD
- Lateral MI (loss of lateral forces)
- Left posterior fascicular block (LPFB); diagnostic criteria:
- right axis deviation > +100 degrees
- leads II, III, aVF but start with a narrow Q (qR)
- leads I and aVL ¯ but start with a small r (rS)
- all other causes of right axis deviation have been excluded
- (isolated LPFB is exceedingly rare; it is a combined clinical and ECG diagnosis)