Sinus P WAVES
Now that you know it is sinus, look for any abnormal Sinus P waves
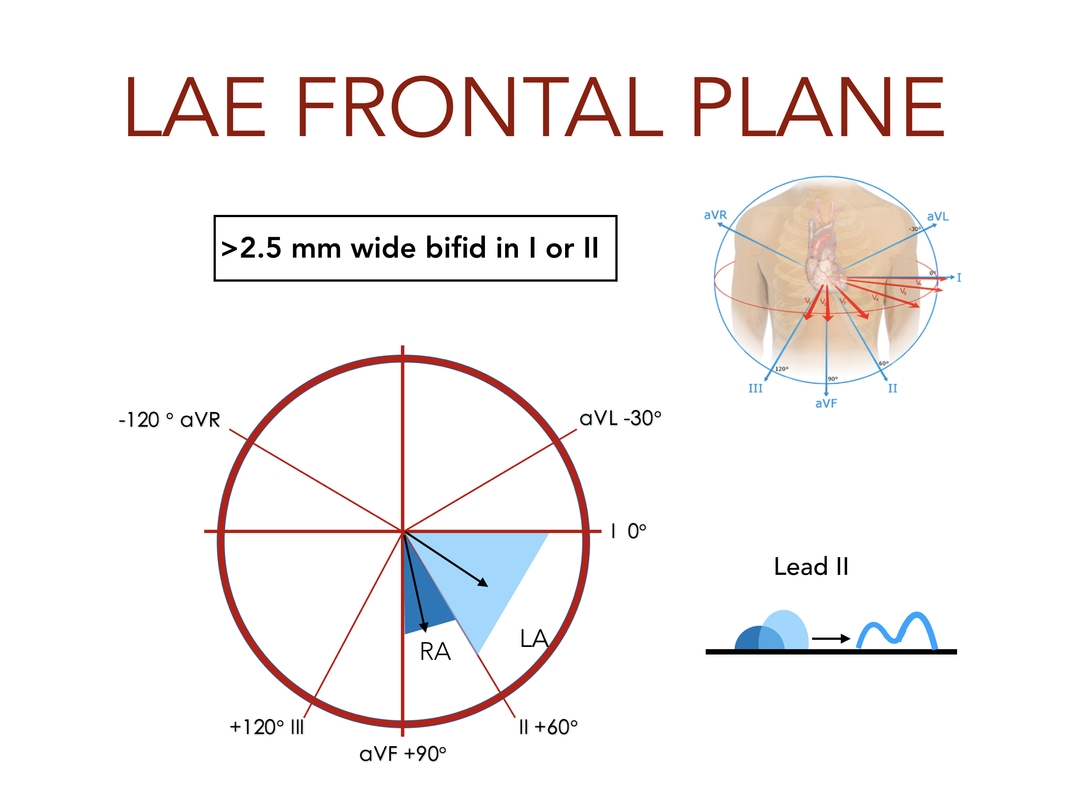
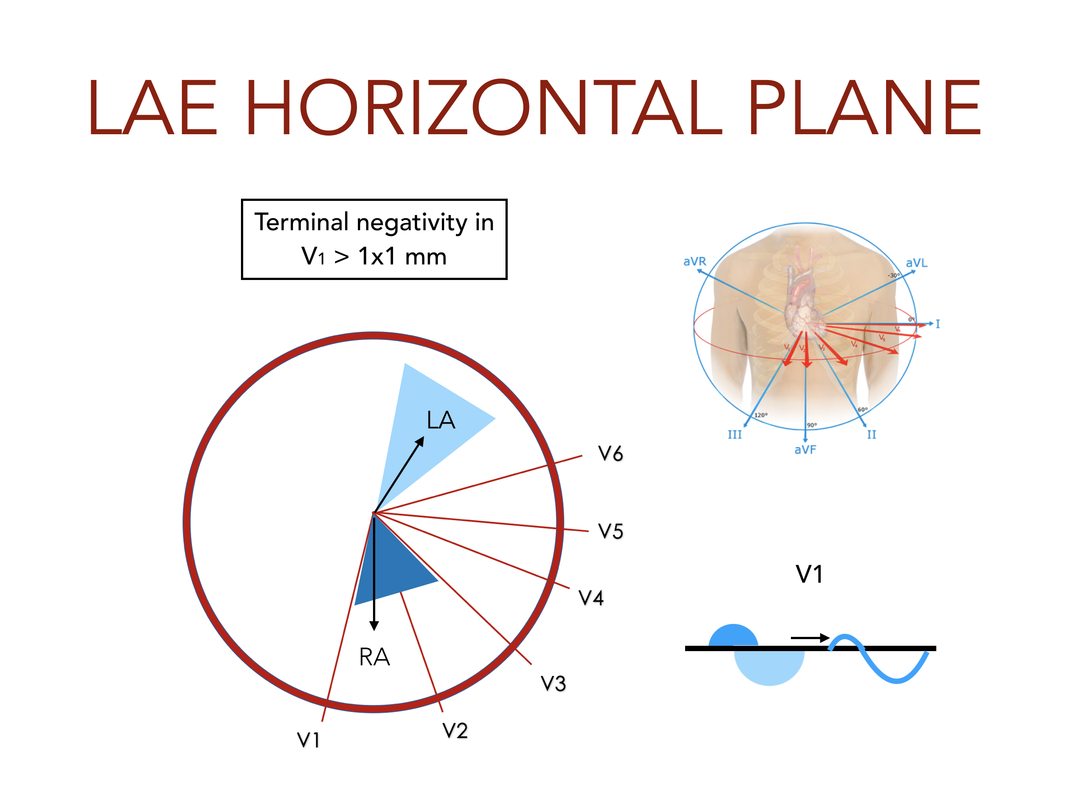
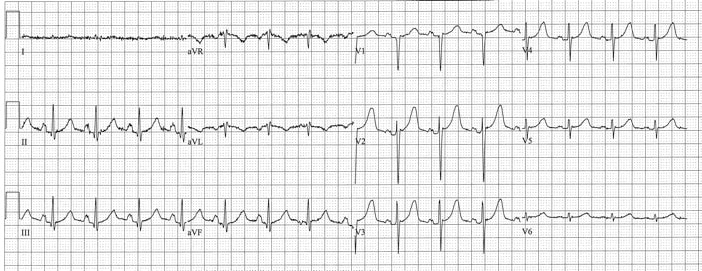
Left Atrial Enlargement
Features:
- V1: Terminal Negativity > 1mm (sensitive, not specific)
- Lead I or II: P wave is wide (>2.5 mm) and bifid (specific, not sensitive)
- 1st degree AV block (PR interval > 5 little boxes, 0.2sec)
- PR segment Depression in II
Clinical Significance of LAE
Findings on of LAE on EKG may suggest
- True left atrial enlargement
- Left atrial hypertrophy
- Left atrial scarring
- Biatrial abnormality
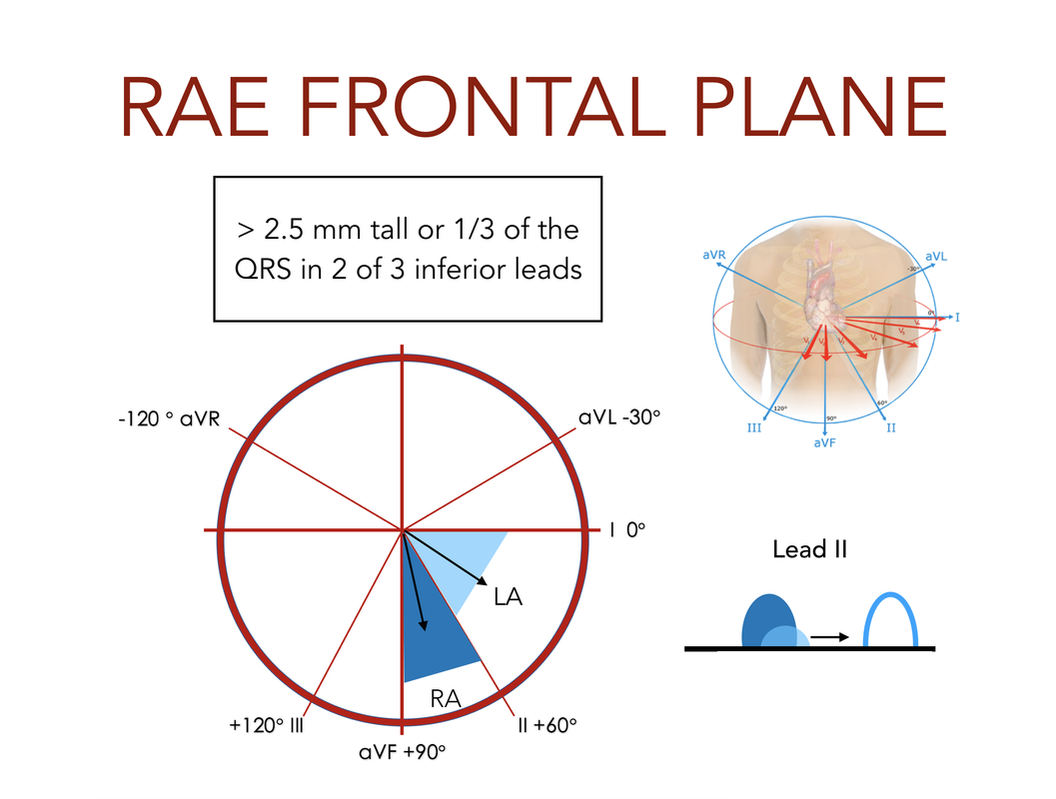
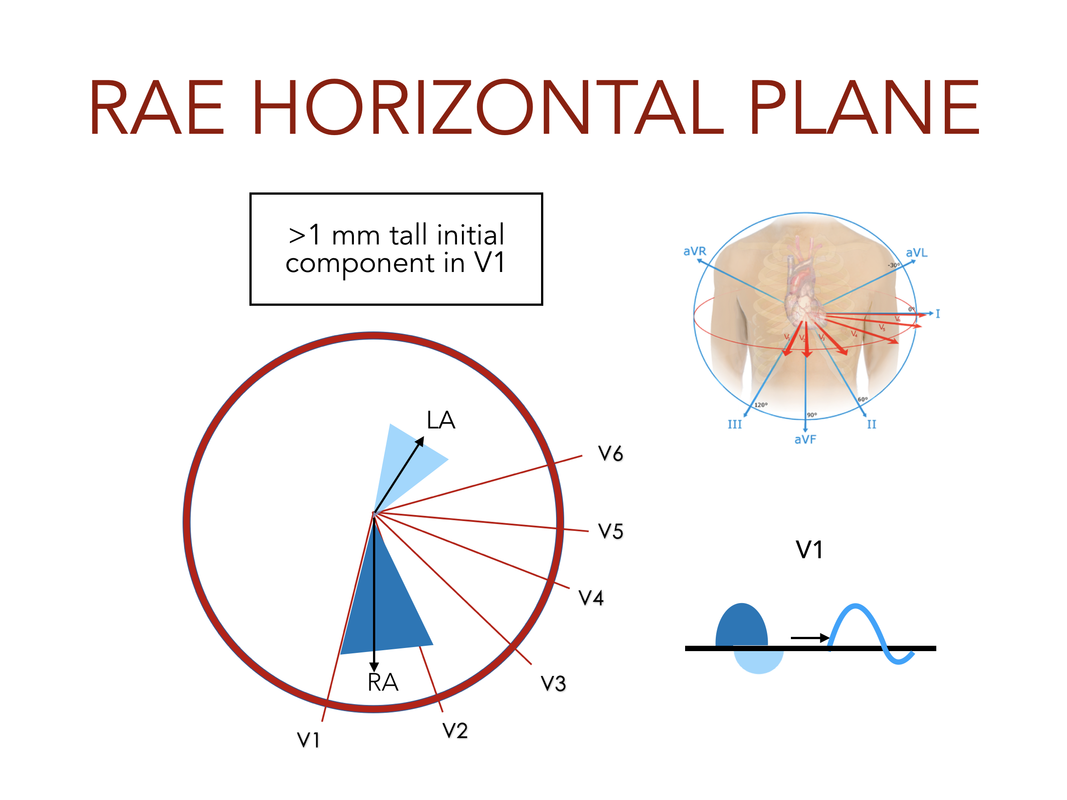
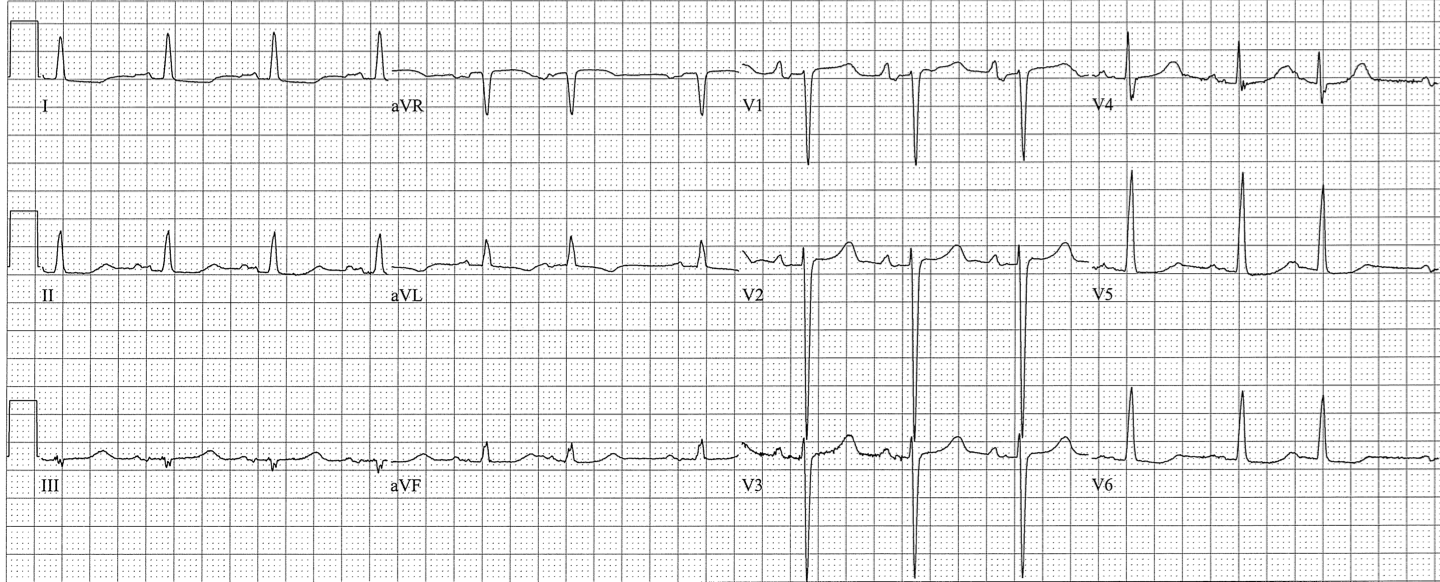
RIGHT ATRIAL ENLARGEMENT
Features
- V1: initial upgoing component > 1mm (specific, not sensitive)
- II, III, aVF: Tall and peaked P (2.5mm or 1/3 QRS height in 2 of 3 (sensitive, not specific)
- Flat line in lead I, and inverted P, QRS in aVL (strongly suggests emphysema)
Clinical Significance of RAE
- RAE suggests pulmonary disease or right heart failure (especially with Reactive Airways)
- Flatline in lead 1 and negative P and QRS in aVL suggests emphysema (vertical lie of the heart)
- RAE is a risk factor for Atrial Flutter
- Sinus Tachycardia is frequently accompanied by tall peaked Ps